Differences between dry and wet carbon fiber molding processes
- Dec-02-2025
- (26) Views
The main differences between dry and wet charcoal lie in manufacturing processes, costs, performance, and application areas.
Manufacturing Process
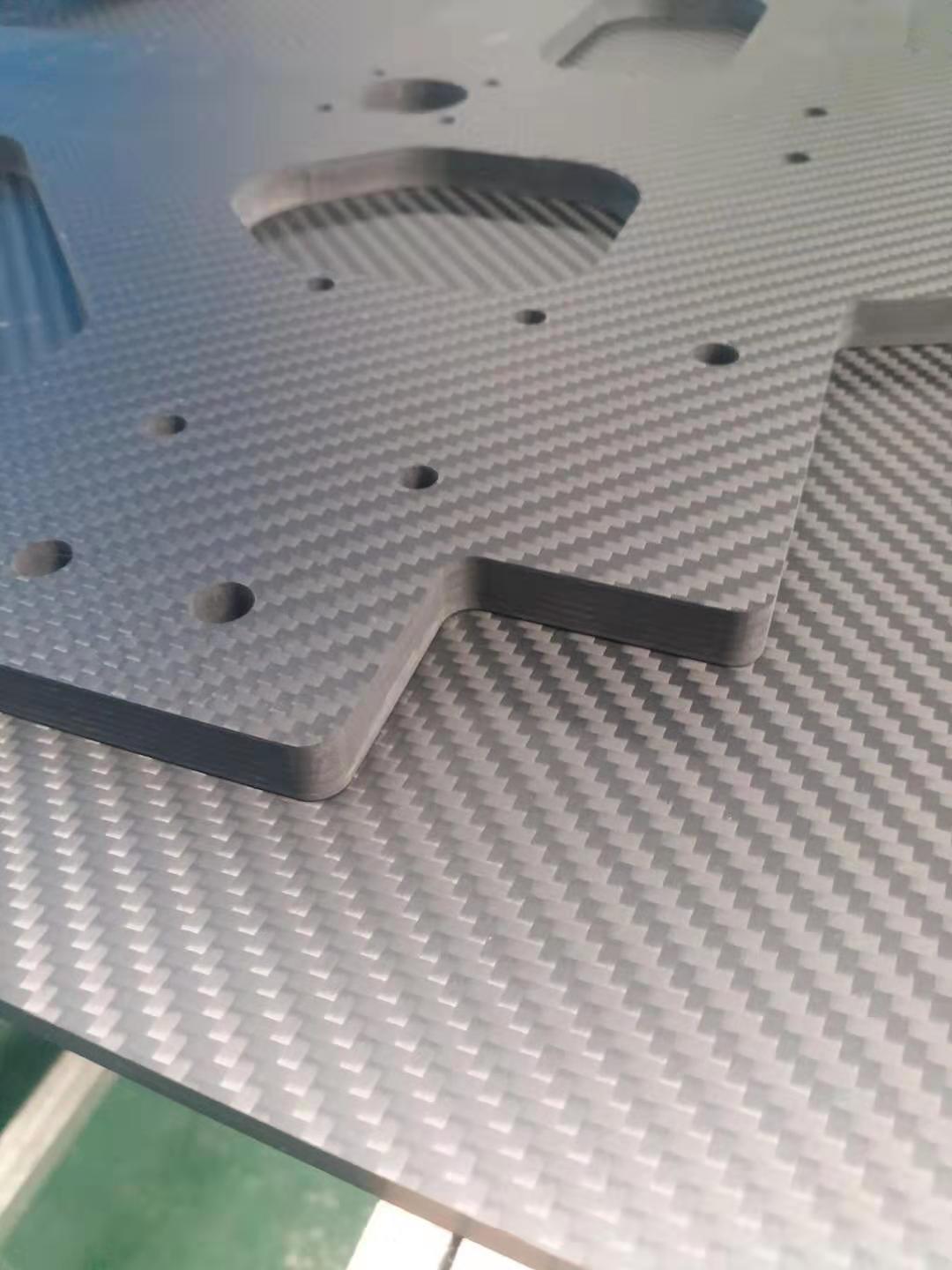
The manufacturing process of dry carbon fiber is relatively complex. It involves placing prepreg of carbon fiber on a high-precision steel mold,
sealing it in a vacuum bag, and then curing it through a thermoforming process. This results in a high degree of compatibility with the original vehicle.
In contrast, the manufacturing process of wet carbon fiber is simpler. It uses molds made of ordinary materials with lower precision.
The carbon fiber cloth is manually soaked in a resin solution, then covered on the mold and cured by heat. This results in a product with slightly lower precision.
Manufacturing Costs
Because the manufacturing process of dry charcoal is more complex and requires more time and materials, it is usually more expensive than wet charcoal.
Product Performance
Dry carbon has less resin residue from the manufacturing process, resulting in parts with higher strength, lighter weight, greater rigidity, and better heat resistance.
Wet carbon, on the other hand, has a higher resin content, leading to relatively lower strength and performance.

Wet Carbon Process: Handmade products are made by low-pressure layering of multiple materials such as black glue, carbon fiber cloth, and gel coat, and then naturally cured at room temperature, resulting in a thicker product.
Dry Carbon Process: Dry carbon consists of two layers of pre-impregnated carbon fiber cloth, hot-pressed at high temperature, resulting in an ultra-thin product with a superior texture.

Handmade unsaturated resin material
Unsaturated products cure at room temperature, have poor oxidation resistance, and are prone to yellowing and matte finish.
Steel mold hot-pressed dry charcoal
Dry charcoal products are high-temperature thermoforming, with epoxy pre-impregnated carbon cloth.
Automotive essential oils, strong resistance to yellowing and oxidation.

Handmade unsaturated resin material
Unsaturated products cure at room temperature, have poor oxidation resistance, and are prone to yellowing and matte finish.
Steel mold hot-pressed dry charcoal
Dry charcoal products are high-temperature thermoforming, with epoxy pre-impregnated carbon cloth.
Automotive essential oils, strong resistance to yellowing and oxidation.
Application Areas
Dry charcoal, due to its superior performance, is primarily used in fields requiring lightweight, high strength, high rigidity, and high heat resistance, such as racing cars, aircraft, and spacecraft.
Wet charcoal, on the other hand, is mainly used in fields requiring aesthetics, durability, and ease of installation, such as automotive modification, bicycles, motorcycles, and sporting equipment.
Furthermore, in terms of appearance, dry charcoal has a smoother, more uniform surface and better abrasion resistance and fade resistance; while wet charcoal may have uneven resin coating,
and the back usually has more noticeable mesh patterns or defects.
 English
English