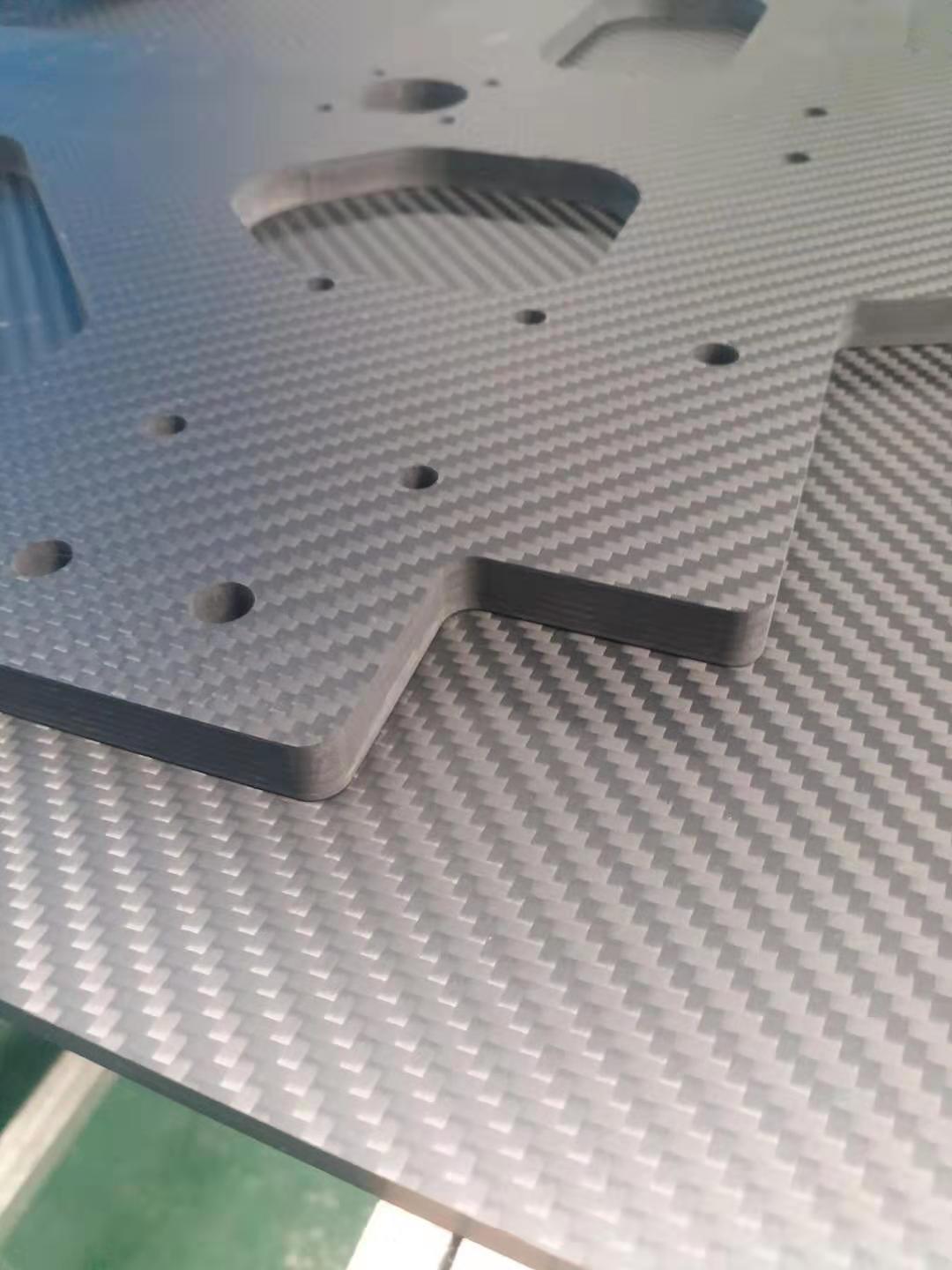
Common Core Material Types and Characteristics in Composite Sandwich Structures
- Dec-02-2025
- (40) Views
Structural core materials are lightweight yet high-strength materials that can be produced from a variety of raw materials, including balsa wood, PVC foam, polyurethane foam, and PET foam. These lightweight materials are bonded between two composite skins and act as the central component of a "sandwich structure." This structure makes composite materials lighter!The face sheets can be made of almost any material. In the composite materials industry, the most common face sheets are fiberglass and carbon fiber sheets. Currently, there are many types of core materials available, with a wide range of performance and cost options. They can be mainly categorized as: light industrial, rigid foam, and honeycomb, etc.
1.Balsa wood,also known as balsa wood, grows in the tropical forests of the Americas. It is one of the fastest-growing trees and the lightest wood in the world. Balsa wood has a high aspect ratio and oriented grains, with the grains aligned towards the direction of maximum stress. Lightweight balsa wood tools have extremely high strength and hardness (by weight); low specific heat, making it less affected by temperature changes;and good fire resistance, heat resistance, and sound insulation properties.

Balsa wood has a good track record in products such as ship hulls, military aircraft, naval vessels, vehicles, wind turbine blades, and corrosion-resistant industrial tanks. For example, the sandwich materials required for wind turbine blades are mainly balsa wood and structural foam materials, which can be used in combination or balsa wood alone.
2.PVC foam board is an alloy foam material based on vinyl polymers and consisting of a network of aromatic amide polymers that runs through it. It is commonly referred to as cross-linked PVC foam core material and is an ideal core material for composite sandwich structures.
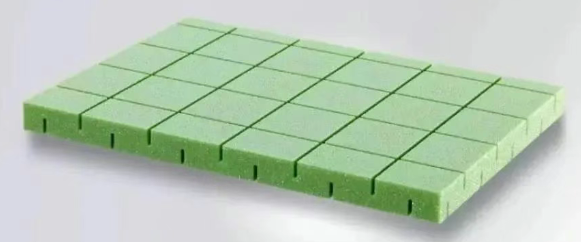
This product boasts excellent comprehensive mechanical properties, stable chemical properties, and the highest cost-effectiveness. With a density range of 40~250 kg/m³, it exhibits excellent specific stiffness and specific strength; good fatigue resistance and impact resistance; thermal insulation; good flame retardancy; low water absorption, making it resistant to moisture and mildew;and good dimensional stability and machinability. It has already found wide application in wind power and marine applications.
3.PU Polyurethane Foam Board
Rigid polyurethane foam is a high-molecular polymer made primarily from isocyanate and polyether, mixed using specialized equipment with the aid of foaming agents, catalysts, flame retardants, and other additives, and then foamed on-site through high-pressure spraying. Polyurethane foam comes in two types: flexible and rigid. Flexible foam has an open-cell structure, while rigid foam has a closed-cell structure. Flexible foam is further divided into skinned and non-skinned types.
4.PET Foam
PET (polyethylene terephthalate) is a lightweight, recyclable thermoplastic. PET foam is a type of closed-cell thermoplastic foam with certain shear and compressive strength, and is therefore often used as the core material in sandwich structures. It is widely used in construction, road transportation, rail transportation, aviation, media, wind power, and other fields.
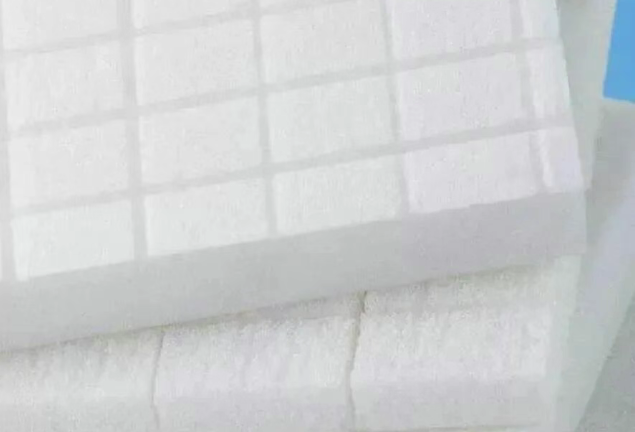

PET foam is characterized by high strength, high temperature resistance, and low price. PET foam core materials also exhibit good fatigue resistance, superior to some PVC foam core materials. In rail transit vehicles, structural foam materials are mainly used in structural floor panels, roofs, side panels, and rear sections. Their main advantages include reduced vehicle weight, thermal insulation, sound insulation, enhanced safety, and fuel cost savings. In shipbuilding, structural foam materials are commonly used in hulls, decks, and superstructures.
5.PMI Structured Foam: Polymethacrylimide (PMI) structured foam is a high-performance foam core material with heat and fire resistance, excellent mechanical properties, and low density. Its disadvantages include relatively high price and limited global production. Applications include aerospace, medical equipment, and communication equipment.

6.Honeycomb
Various types of man-made honeycomb cores are widely used in the aerospace and transportation industries. Honeycomb materials include paper, aluminum, phenolic resin-impregnated glass fibers, polypropylene, and aramid fibers treated with phenolic resin. Densities range from 1 to 6 lbs/fᶟ. Physical properties depend heavily on the specific material and density. Honeycomb cores can be used to create extremely lightweight panels.

7.Fiber-Reinforced Core
Fiber-reinforced composite core technology combines glass fiber and closed-cell foam in an engineered structure to create a highly effective sandwich solution with very high mechanical properties. It is ideal for use as a material in static applications requiring high stiffness and can also replace wood and plywood.
 English
English