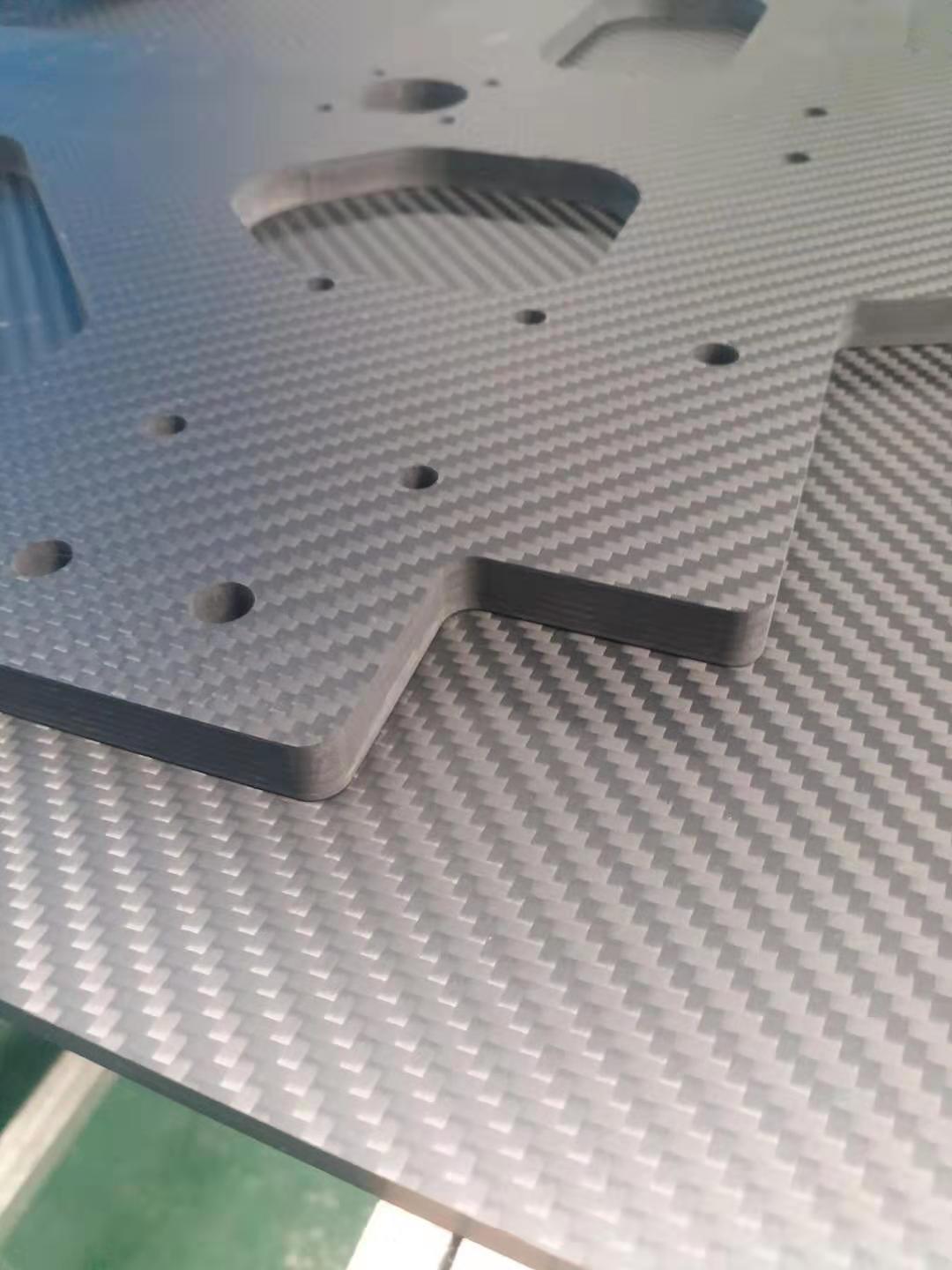
Five key properties of carbon fiber prepreg
- Dec-08-2025
- (32) Views
Resin content
Definition: The percentage of the total mass of resin, curing agent, and various modifiers in a prepreg.Importance: Directly affects the fiber volume fraction (FVF) of the final composite component, which is a core parameter determining the material's mechanical properties (strength, modulus).
Volatile content
Definition: The mass percentage of volatile substances (mainly residual solvents, moisture, and small-molecule reaction byproducts) in a prepreg.Importance: The volatile components in a prepreg mainly originate from low-molecular-weight substances and solvents in the resin. An appropriate amount of volatile components allows the resin to have a certain degree of fluidity during molding, while a high volatile content will result in a higher porosity in the molded composite material.
Viscosity
Definition: Adhesion between prepreg layers, or between prepreg and mold surface, under certain temperature and pressure conditions.Importance: Adhesion is a crucial processing property of prepregs. During transportation and storage, the first sign of deterioration in prepreg performance is a decrease in adhesion. Generally, unacceptable adhesion indicates that the prepreg has exceeded its shelf life. Therefore, adhesion is a vital quality control indicator for prepregs and a primary basis for determining shelf life.
Resin flow
Definition: Used to characterize the resin's flowability during molding.Importance: Low flowability makes it difficult for the resin to penetrate into the fibers, often resulting in poor contact between layers in the product; high flowability often leads to severe resin flow during curing, reducing the resin content of the product and potentially affecting the fiber orientation in the part. Appropriate flowability can expel air between layers, reducing the porosity of the composite material.
Gel time
Definition: The time required for a resin to complete its reaction and cure is a crucial parameter in composite material molding processes.Importance: Its properties determine molding stability, influence material properties, and affect storage life; it is key to ensuring the quality and application performance of composite materials.
 English
English