Pultrusion process
- Dec-10-2025
- (30) Views
Pultrusion is a continuous manufacturing method for composite profiles. It involves impregnating untwisted glass fiber rovings and other continuous reinforcing materials, such as polyester surface mats, with resin. The impregnated materials are then passed through a forming die that maintains a specific cross-sectional shape, where they are cured and continuously extruded from the mold. This process results in the automated production of pultruded products.
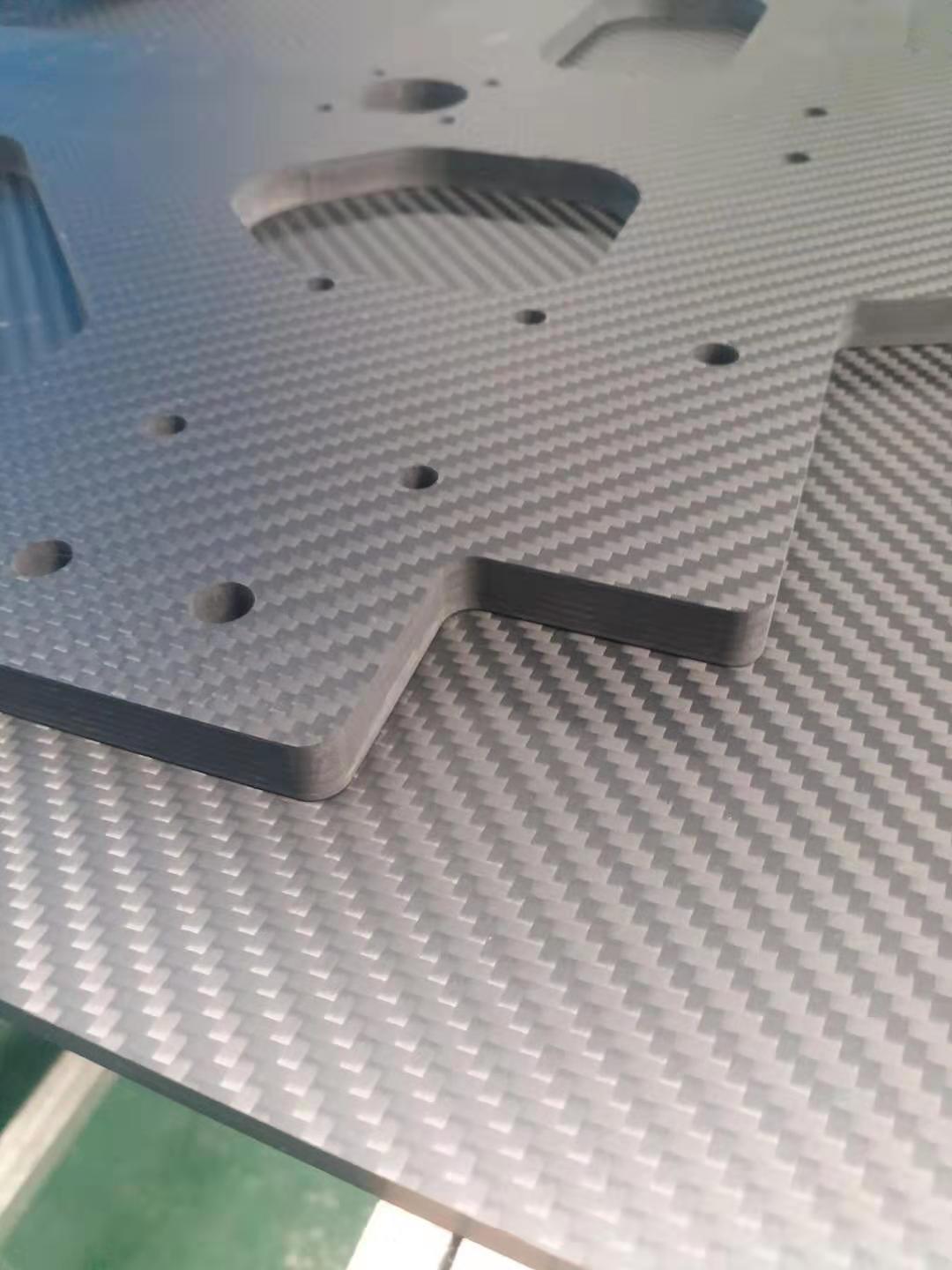
Products manufactured using the pultrusion process have higher tensile strength than ordinary steel. The resin-rich surface layer also provides excellent corrosion resistance, making them the ideal replacement for steel in corrosive environments. They are widely used in transportation, electrical engineering, electrical insulation, chemical industry, mining, marine applications, shipbuilding, corrosive environments, and various civil and domestic applications.
Pultrusion process flow
There are many forms of pultrusion processes and many ways to classify them. Examples include intermittent and continuous processes, vertical and horizontal processes, wet and dry processes, caterpillar-type and clamping-type traction, in-mold curing and in-mold gelation followed by external curing, and heating methods such as electric heating, infrared heating, high-frequency heating, microwave heating, or a combination of these.
The typical pultrusion process flow is as follows:
Glass fiber roving arrangement — impregnation — preforming — extrusion molding and curing — pulling — cutting — finished product.
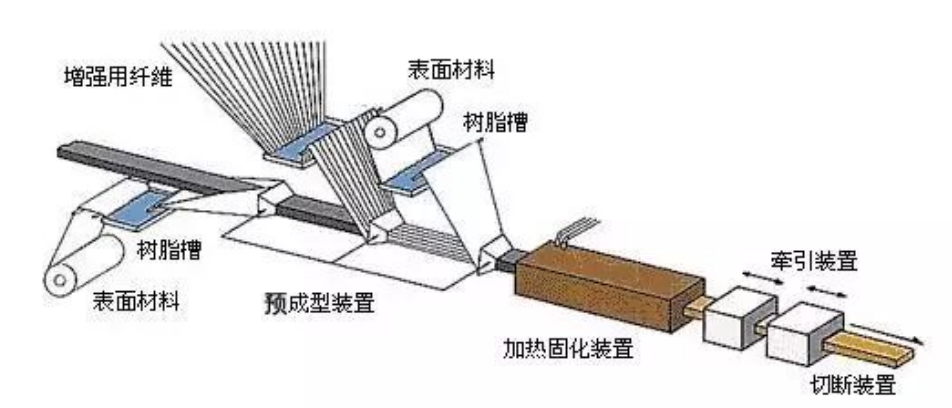
Pultrusion equipment components:
Enhanced Material Feeding System: such as yarn racks, felt spreading devices, and yarn guides
Resin Impregnation: The straight-channel impregnation method is the most commonly used. During the entire impregnation process, the fibers and felt should be arranged very neatly.
Preforming: The impregnated reinforcing material passes through the preforming device, carefully conveyed in a continuous manner to ensure their relative positions, gradually approaching the final shape of the product, and extruding excess resin before entering the mold for molding and curing.
Mold: The mold is designed under the conditions determined by the system. Based on the resin curing exothermic curve and the friction properties between the material and the mold, the mold is divided into three different heating zones, whose temperatures are determined by the performance of the resin system. The mold is the most critical part of the pultrusion process; typical mold lengths range from 0.6 to 1.2 meters.
Pulling Device: The pulling device itself can be a caterpillar-type puller or two reciprocating clamping devices to ensure continuous movement. 6. Cutting Device: The profile is cut to the required length by an automatically synchronized moving cutting saw.
 English
English