The manufacturing process of carbon fiber composite materials
- Jan-07-2026
- (21) Views
Carbon fiber composite material is a high-performance composite material composed of carbon fibers and a resin matrix. It possesses advantages such as high strength, high modulus, low density, corrosion resistance, and fatigue resistance, and is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods industries.
Pretreatment of Carbon Fibers
Before preparing carbon fiber composites, carbon fibers need to be pretreated to improve their surface activity and compatibility with the resin matrix. There are many pretreatment methods, such as oxidation treatment, anodic oxidation treatment, and plasma treatment. Among these, oxidation treatment is one of the most commonly used methods.
Oxidation treatment involves exposing the carbon fibers to air or oxygen at a certain temperature and for a certain time to form an oxide film on their surface. This oxide film can increase the surface roughness and specific surface area of the carbon fibers, thereby improving their bonding strength with the resin matrix. The conditions for oxidation treatment are typically 200-400°C for 1-10 hours.
Preparation of Resin Matrix
The resin matrix is an important component of carbon fiber composite materials and can be divided into two main categories: thermosetting resins and thermoplastic resins. Thermosetting resins are those that undergo a curing reaction during heating, forming a three-dimensional network structure, such as epoxy resins, polyester resins, and phenolic resins. Thermoplastic resins are those that soften or melt during heating, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and nylon.
When preparing the resin matrix, it is necessary to select a suitable resin based on the performance requirements and operating environment of the carbon fiber composite material, and to mix the resin and curing agent uniformly in a certain proportion. Mixing methods include mechanical stirring, ultrasonic stirring, and vacuum stirring. The mixed resin matrix needs to be degassed at a certain temperature to remove air bubbles.
Carbon Fiber and Resin Matrix Compositing
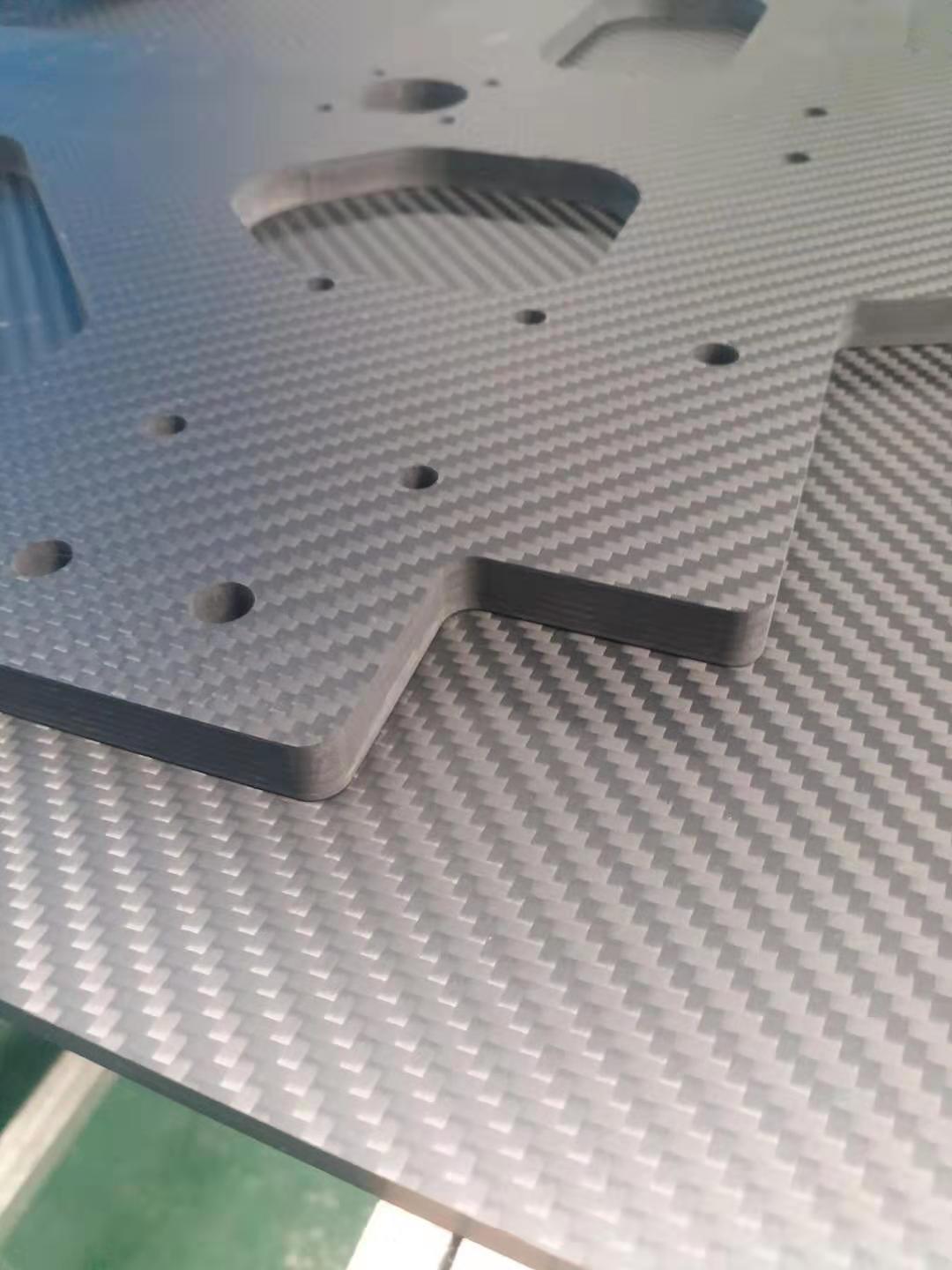
The compositing of carbon fibers with a resin matrix is a crucial step in the preparation of carbon fiber composite materials, directly affecting the performance and quality of the composite. There are many methods for compositing, such as hand lay-up, spraying, molding, and filament winding. Among these, hand lay-up is one of the simplest and most commonly used methods.
The hand lay-up method involves laying pre-treated carbon fibers and resin matrix layer by layer onto a mold, and then pressing them flat with a spatula or brush to remove air bubbles. Each layer requires curing to solidify the resin and form a hard layer. This process is repeated until the desired thickness is achieved. Finally, the mold is removed from the composite material, and the material is trimmed and processed.
Curing of Carbon Fiber Composites
Curing of carbon fiber composites refers to the process of subjecting the composite material to a curing reaction at a specific temperature and time, allowing the resin matrix to form a rigid three-dimensional network structure. The curing conditions depend on the type and proportion of the resin matrix and curing agent used, as well as the thickness and shape of the composite material.
Generally, the curing temperature is 120-180°C, and the time is 1-2 hours. During the curing process, the temperature and time need to be carefully controlled to avoid over-curing or under-curing. Over-curing can lead to embrittlement of the resin matrix, reducing the mechanical properties of the composite material; under-curing can result in incomplete curing of the resin matrix, affecting the stability and durability of the composite material.
Post-processing of Carbon Fiber Composites
Post-processing of carbon fiber composites refers to further processing and modification of the cured composite material to improve its appearance and performance. There are many post-processing methods, such as grinding, polishing, cutting, drilling, and painting. Among these, grinding and polishing are among the most commonly used methods.
 English
English